学习要点:
1、url拼接
2、通过xpath helper获得xpath路径
3、学习爬虫的整个流程,绿色的箭头代表数据流。
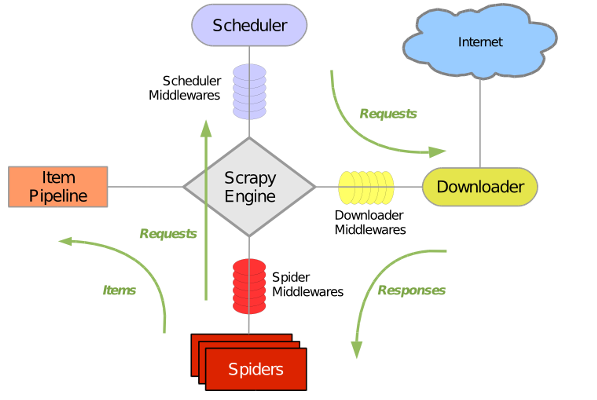
标记一下:
整理文章内文:
'/n'.join([p.text.strip() for p in soup.select('#artibody p')[:-1]])
一、创建项目
进入到要工作目录,执行scrapy startproject Tencent
二、创建爬虫
进入Tencent,再进入Tencent目录,运行以下命令,生成一个爬虫
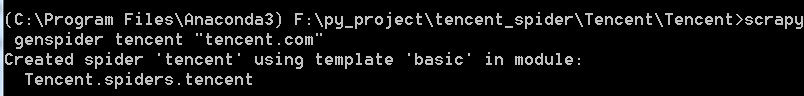
注意:
这里的爬虫名称不能和项目名称相同,否则会报错:
Cannot create a spider with the same name as your project
上图中项目名称是“Tencent”,爬虫名称是“tencent”,大小写不同,所以才没有报错,不过建议项目名称用tencent,爬虫名称用tencentSpider这样的形式。
这里虽然是在\tencent\tencnet\目录下执行这个命令,但是创建的爬虫文件是直接保存到了spider目录下面。
三、设定item
用pycharm打开项目,修改item.py
class TencentItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
#职位名称
positionName = scrapy.Field()
#职位详情链接
positionLink = scrapy.Field()
#职位类别
positionType = scrapy.Field()
#招聘人数
peopleNumber = scrapy.Field()
#工作地点
workLocation = scrapy.Field()
#发布时间
publishTime = scrapy.Field()
四、编写爬虫文件
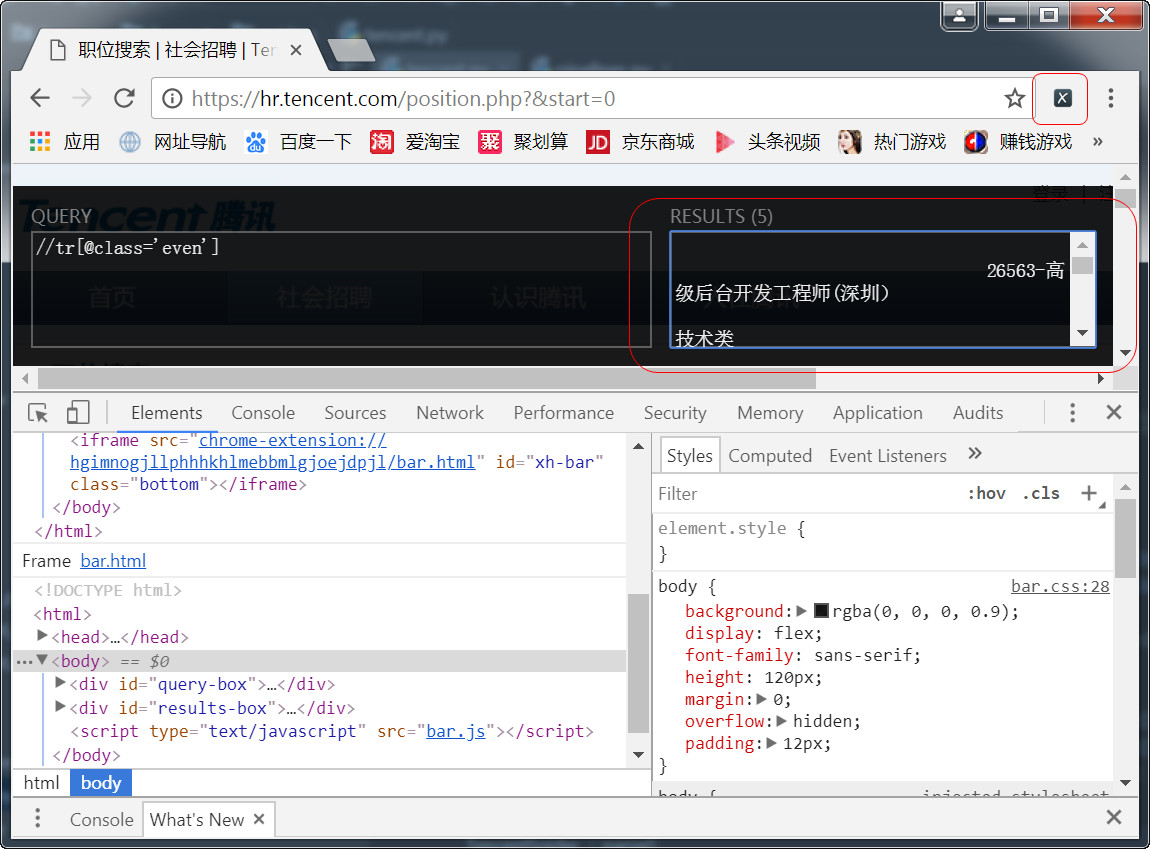
在这一步,可以利用chrome的插件xpath helper选择节点的xpath路径。
蜗牛博客备注:
xpath可以在最新版本的chrome浏览器中使用,最好通过翻墙的方式,直接就可以安装。
import scrapy
from Tencent.items import TencentItem
class TencentSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["tencent.com"]
baseUrl = "https://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start="
offset = 0
start_urls = [baseUrl + str(offset)]
#用来处理response
def parse(self, response):
node_list = response.xpath("//tr[@class='even'] | //tr[@class='odd']")
for node in node_list:
item = TencentItem()
item['positionName']= node.xpath("./td[1]/a/text()").extract()[0]
item['positionLink'] = node.xpath("./td[1]/a/@href").extract()[0]
if len(node.xpath("./td[2]/text()")):
item['positionType'] = node.xpath("./td[2]/text()").extract()[0]
else:
item['positionType'] = ""
item['peopleNumber'] = node.xpath("./td[3]/text()").extract()[0]
item['workLocation'] = node.xpath("./td[4]/text()").extract()[0]
item['publishTime'] = node.xpath("./td[5]/text()").extract()[0]
#yield的重要性,是返回数据后还能回来接着执行代码
yield item
五、编写管道文件
处理spider返回的item数据
import json
class TencentPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
self.f = open("tencent.json", "w")
def process_item(self, item, spider):
content = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + "\n"
self.f.write(content)
return item
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.f.close()
六、setting文件
启用pipeline,这一步非常简单,只需要将以下代码解除注释即可。
# Configure item pipelines
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'Tencent.pipelines.TencentPipeline': 300,
}
七、完善爬虫文件
在爬虫文件的末尾加入以下代码。
spider方法主要有两个:一个返回保存数据,一个返回需要继续爬取的页面请求,请求不需要我们处理,我们只要将请求构建好就可以了,发给引擎,引擎让调度器去重、入队列,交给下载器,下载器返回的响应文件,用callback处理。
if self.offset <= 3939:
self.offset += 10
url = self.baseUrl + str(self.offset)
yield scrapy.Request(url, callback=self.parse)
八、运行爬虫
九、第二种方法
将tencent.py末端代码改成下面这样:
if len(response.xpath("//a[@class='noactive' and @id='next']")) == 0:
url = response.xpath("//a[@id='next']/@href").extract()[0]
yield scrapy.Request("http://hr.tencent.com/" + url, callback=self.parse)
十、json文件
这样保存的json文件并不是标准的json格式,需要将末尾的逗号去掉,然后用中括号括起来,就可以在json.cn这样的JSON在线解析及格式化验证网站查看。

原载:蜗牛博客
网址:http://www.snailtoday.com
尊重版权,转载时务必以链接形式注明作者和原始出处及本声明。

